It is invariably accepted that data handling can improve business decisions and management. What if it goes the other way around, too? Quality management within a company allows for comprehensive and systematic documentation of day-to-day activities, recorded accurately and timely, with proper organization, producing a richer dataset to work with. Analysis and modeling are only as good as the data, and data will be as good as the quality management system of the business.
In this article, we attempt to map out how the management system in place leads to better decision-making via data handling. This process is summarized in the following diagram, and explained below.
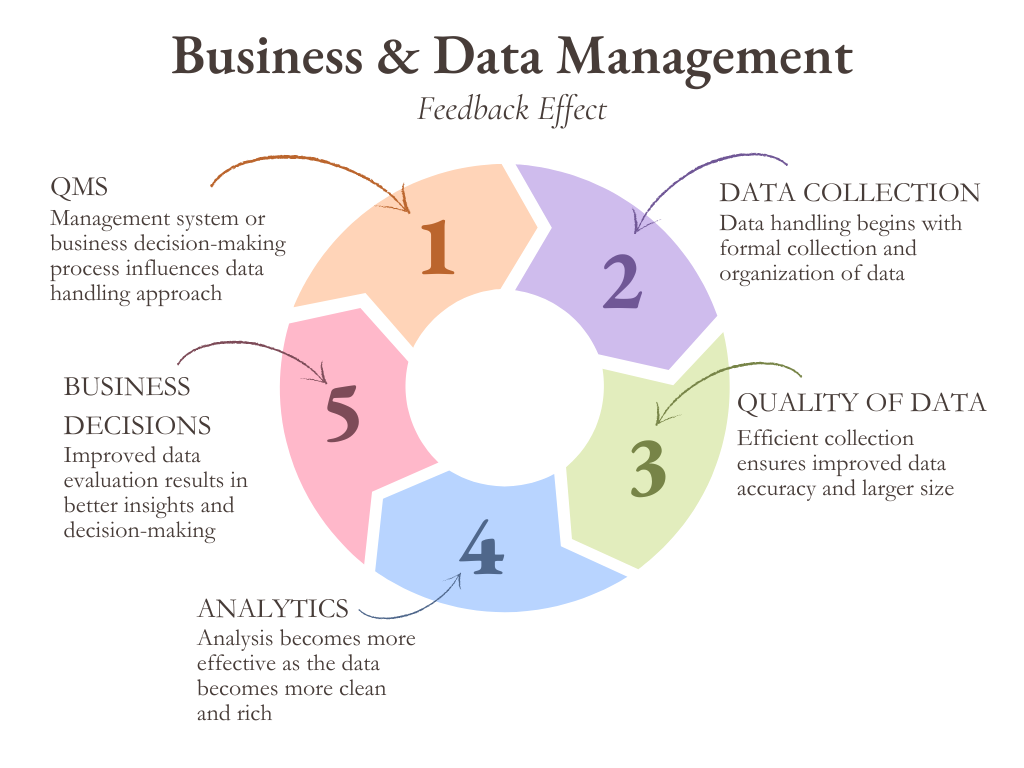
-
Quality Management System (QMS)
The management system defines the structural and operational elements of how a business works and makes decisions. The objective is to ensure the quality of the processes, procedures, and responsibilities involved in delivering products and services to customers. These are determined mainly by benchmark standards of business management, relevant to the field the business is operating in. An innovative addition to a managerial structure and/or operation further boosts the efficiency and effectiveness of the entire business set-up.
Data management is a crucial constituent of the management system. Adopting the best practices relating to data handling, which is encouraged in a quality management system, facilitates systematic data collection and organization.
-
Data Collection & Organization
A QMS-driven business intuitively befriends the concept of data, which is usually incoherent in its raw form. In data handling, the first step concerns the collection, storage, and organization of business data.
Data is a dynamic entity. It is produced day in, day out. By using proper procedures and tools, valuable data can be collected from different sources and stored in modifiable data repositories for future evaluation. Systematic collection and organization of data, promoted by the quality management system, help capture the ins and outs of raw data. Moreover, a quality approach to data management ensures that the raw data stored, which is originally “out there” in a chaotic shape, is “taken in” in a processable and analyzable form.
-
Quality of Data
A systematic approach to collecting, storing, and organizing data – accompanied by the technological apparatus used – ensures the quality of data available to businesses. Data quality is evaluated on the following elements:
- Accuracy (reliable sources and methodology of collection),
- Consistency (uniformity of data collected over time and through different sources),
- Validity & Usefulness (applicable to business problems),
- Completeness (contains relevant variables and usable records), &
- Dynamism (updated timely).
Compared to data collected haphazardly, quality data allows for easier pre-processing and applicability options, which are essential in the analysis phase.
-
Analytics
Data analytics is the process of converting data collected to useful information. Involving different analysis and modeling processes, this step consists of applying technical and visual procedures to find quantitative and hidden trends, patterns, and correlations within the data. Advanced modeling may include causality, forecasting, and prediction.
Hard skills are an important requirement for extracting valuable information from raw data. A quality management system, noting this, equips their business procedures with adequate talent and the latest technology to achieve more significant insights.
-
Decision-Making
Once the analysts finalize and present the findings (to top management), these insights and recommendations are prudently understood with business acumen and strategically applied to the business problem. This process of translating insights from data analytics into actionable practices is not only encouraged in a QMS, but it also strengthens the structural and operational efficiency of the management system itself. It acts as a reinforcing loop: the QMS initiating data handling becomes more aware and equipped by the results.
Soft skills are a fundamental asset of top management, which helps in business decision-making. A quality management system, understanding this, integrates capacity building into its model.






